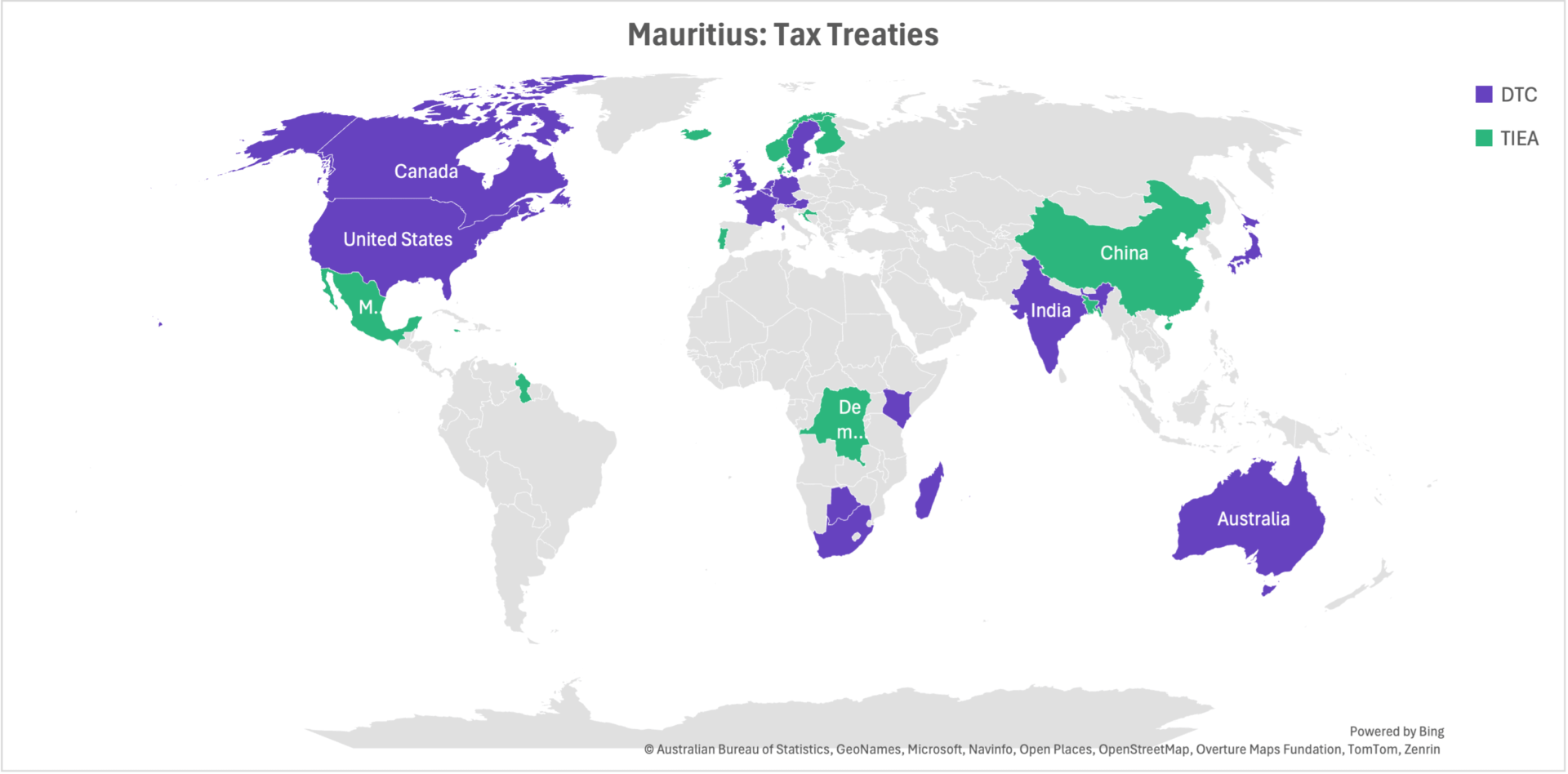
he Republic of Mauritius has become one of the richest countries in Africa. Tourism, trade, IT, and financial sectors are developed here. This has been facilitated by signing several agreements and joining the WTO, COMESA, South African Customs Union (SACU), and Organization of African Unity (OAU). More than 50 double taxation treaties have been concluded. To confirm the reliability of the jurisdiction, the country’s legislation is designed to meet the requirements of FATF and the EU.
The geographical location has positively impacted Mauritius’s economy and turned it into an international logistics center for trade between Africa and Asia. The state is also effectively developing export-import ties with China and the USA.
The chosen economic strategy of the authorities, the simplicity of company registration, optimal tax benefits for offshore business, and the possibility of developing global business ties have stimulated a large inflow of capital into this jurisdiction. Registration of companies in Mauritius is carried out by the Legal Entities and Business Registration Division (CBRD) under the Ministry of Finance based on the Companies Act 2001 and Business Registration Act 2002.
Once a company is registered, it enjoys several benefits, including zero capital gains tax, optimal corporate tax, no exchange controls, and a guarantee of data confidentiality.